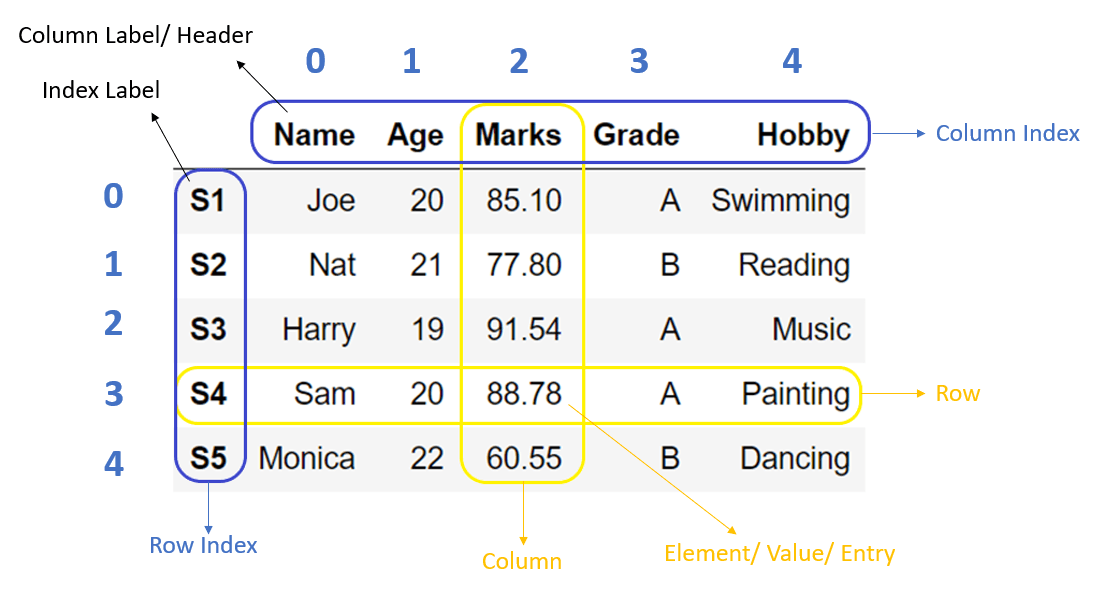
43 indexing using labels in dataframe
› python-pandas-dataframePython | Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks Jan 10, 2019 · Indexing a DataFrame using .loc[ ]: This function selects data by the label of the rows and columns. The df.loc indexer selects data in a different way than just the indexing operator. It can select subsets of rows or columns. It can also simultaneously select subsets of rows and columns. Selecting a single row Working With Specific Values In Pandas DataFrame - Data Courses This function of a pandas DataFrame is of high value as you can build an index using a specific column, (meaning: a label) that you want to use for managing and querying your data. For example, one can develop an index from a column of values and then use the attribute.loc to select data from pandas DataFrame based on a value found in the index.
Indexing, Slicing and Subsetting DataFrames in Python When using loc, integers can be used, but the integers refer to the index label and not the position. For example, using loc and select 1:4 will get a different result than using iloc to select rows 1:4. We can also select a specific data value using a row and column location within the DataFrame and iloc indexing:

Indexing using labels in dataframe
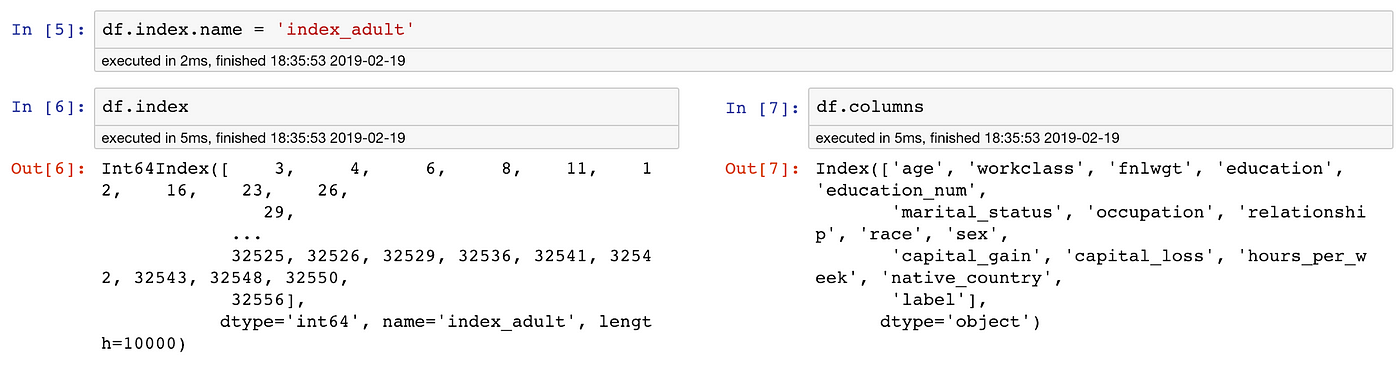
Pandas DataFrame Indexing - KDnuggets In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on. Pandas DataFrame Indexing: Set the Index of a Pandas Dataframe In this method, we can set the index of the Pandas DataFrame object using the pd.Index() and set_index() function. First, we will create a Python list then pass it to the pd.Index() function which returns the DataFrame index object. Then we pass the returned DataFrame index object to the set_index() function to set it as the new index of the DataFrame. Let's implement this through Python code. Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.4.4 documentation pandas provides a suite of methods in order to have purely label based indexing. This is a strict inclusion based protocol. Every label asked for must be in the index, or a KeyError will be raised. When slicing, both the start bound AND the stop bound are included, if present in the index.
Indexing using labels in dataframe. Indexing Dataframes. Indexing Dataframes in Pandas | by Vidya Menon ... loc Method: It is one of the most versatile methods in pandas used to index a dataframe and/or a series method.The loc () function is used to access a group of rows and columns by label (s) or a boolean array. loc [] is primarily label based, but may also be used with a boolean array. The syntax being: Modifying Values in DataFrames: Label Indices - Real Python So with .loc, the key thing to remember is that the actual values that you pass in to .loc have to be the actual labels of either the row and the column. 04:32 However, sometimes you may want to access the values of a DataFrame or the rows or columns using integer indices, and this is what we'll talk about in the next lesson. Pandas: Create an index labels by using 64-bit integers ... - w3resource Pandas Indexing: Exercise-4 with Solution Write a Pandas program to create an index labels by using 64-bit integers, using floating-point numbers in a given dataframe. Test Data: › python › examplesHow to Subset a DataFrame in Python? - AskPython This line of code selects rows from 1 to 7 and columns corresponding to the labels ‘population’ and ‘housing’. Subset a Dataframe using Python iloc() iloc() function is short for integer location. It works entirely on integer indexing for both rows and columns. To select a subset of rows and columns using iloc() use the following line ...
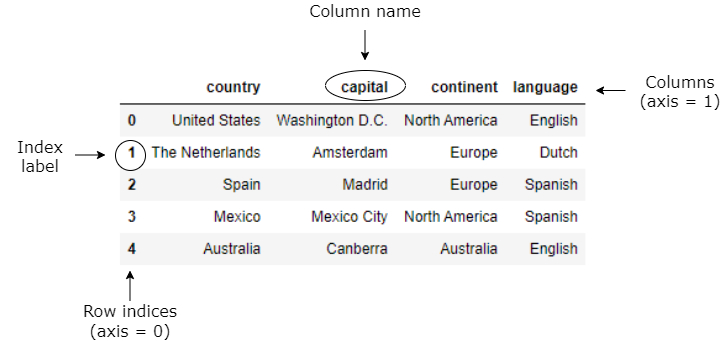
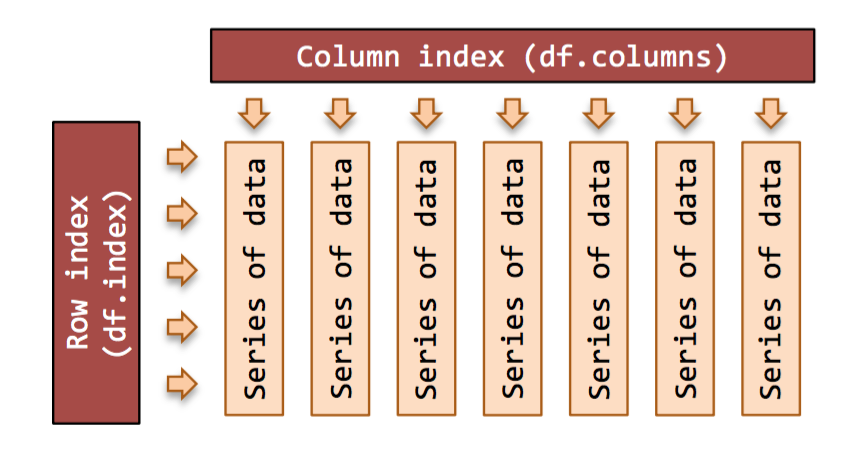
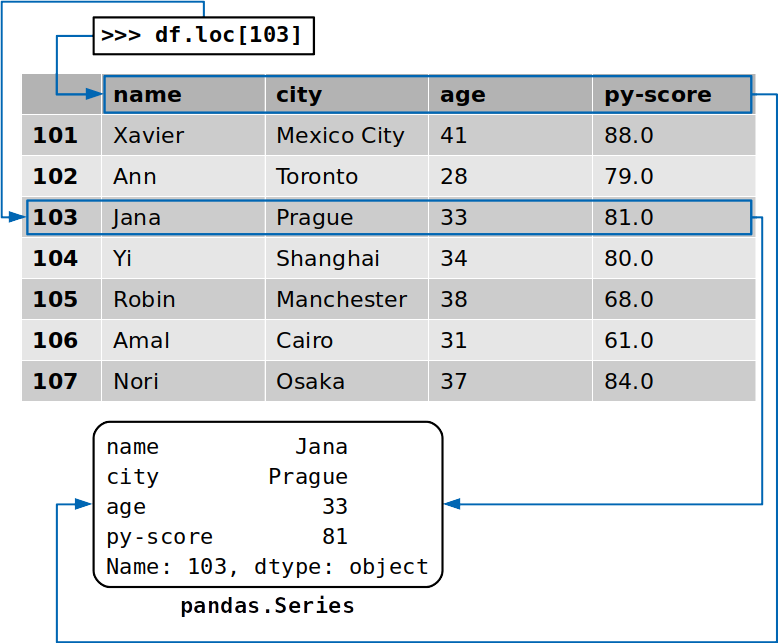
Boolean Indexing in Pandas - tutorialspoint.com Practical Data Science using Python. Boolean indexing helps us to select the data from the DataFrames using a boolean vector. We need a DataFrame with a boolean index to use the boolean indexing. Let's see how to achieve the boolean indexing. Create a dictionary of data. Convert it into a DataFrame object with a boolean index as a vector. Indexing and Selecting Data with Pandas - GeeksforGeeks These indexing methods appear very similar but behave very differently. Pandas support four types of Multi-axes indexing they are: Dataframe.[ ] ; This function also known as indexing operator; Dataframe.loc[ ]: This function is used for labels. Dataframe.iloc[ ]: This function is used for positions or integer based; Dataframe.ix[]: This function is used for both label and integer based; Collectively, they are called the indexers. These are by far the most common ways to index data. What does the pandas DataFrame.index attribute do? - tutorialspoint.com In pandas.DataFrame the row labels are called indexes, If you want to get index labels separately then we can use pandas.DataFrame "index" attribute. Example 1 In this example, we have applied the index attribute to the pandas DataFrame to get the row index labels. realpython.com › pandas-dataframeThe Pandas DataFrame: Make Working With Data Delightful This Pandas DataFrame looks just like the candidate table above and has the following features: Row labels from 101 to 107; Column labels such as 'name', 'city', 'age', and 'py-score' Data such as candidate names, cities, ages, and Python test scores; This figure shows the labels and data from df:
Finding label location in a DataFrame Index - Stack Overflow Finding label location in a DataFrame Index. import pandas as pnd d = pnd.Timestamp ('2013-01-01 16:00') dates = pnd.bdate_range (start=d, end = d+pnd.DateOffset (days=10), normalize = False) df = pnd.DataFrame (index=dates, columns= ['a']) df ['a'] = 6 print (df) a 2013-01-01 16:00:00 6 2013-01-02 16:00:00 6 2013-01-03 16:00:00 6 2013-01-04 ... Pandas : Sort a DataFrame based on column names or row index labels ... In the Python Pandas Library, the Dataframe section provides a member sort sort_index () to edit DataFrame based on label names next to the axis i.e. DataFrame.sort_index (axis=0, level=None, ascending=True, inplace=False, kind='quicksort', na_position='last', sort_remaining=True, by=None) Where, re-thought.com › delete-drop-column-from-pandasDelete column/row from a Pandas dataframe using .drop() method Feb 02, 2020 · Columns can be removed permanently using column name using this method df.drop(['your_column_name'], axis=1, inplace=True). To drop a single column from pandas dataframe, we need to provide the name of the column to be removed as a list as an argument to drop function. Remember parameter self? Pandas .drop() function can drop column or row. A Step 2: Set a single column as Index in Pandas DataFrame. Use merge. By default, this performs an inner join. pd.merge(df1, df2, left_ index =True, right_ index =True). Boolean indexing is a type of indexing which uses actual values of the data in the DataFrame. In boolean indexing, we can filter a data in four ways -.
› boolean-indexing-in-pandasBoolean Indexing in Pandas - GeeksforGeeks Jun 08, 2022 · Accessing a Dataframe with a boolean index using .ix[] In order to access a dataframe using .ix[], we have to pass boolean value (True or False) and integer value to .ix[] function because as we know that .ix[] function is a hybrid of .loc[] and .iloc[] function. Code #1:
pandas.DataFrame.set_index — pandas 1.4.4 documentation Set the DataFrame index using existing columns. Set the DataFrame index (row labels) using one or more existing columns or arrays (of the correct length). The index can replace the existing index or expand on it. Parameters. keyslabel or array-like or list of labels/arrays. This parameter can be either a single column key, a single array of the ...
datacarpentry.org › python-ecology-lesson › 03-indexIndexing, Slicing and Subsetting DataFrames in Python Indexing by labels loc differs from indexing by integers iloc. With loc, both the start bound and the stop bound are inclusive. When using loc, integers can be used, but the integers refer to the index label and not the position. For example, using loc and select 1:4 will get a different result than using iloc to select rows 1:4.
Accessing columns of a DataFrame using column labels in Pandas - SkyTowner Accessing multiple columns. The only difference with the single-case is that here we pass in a list of column labels as opposed to a single string. Access and update values of the DataFrame using row and column labels. To access columns of a DataFrame using integer indices in Pandas, use the DataFrame.iloc.
Indexing and Sorting a dataframe using iloc and loc Integer based indexing using iloc. To select some fixed no. of column and a fixed no. of rows from this data, one way is to achieve it by using iloc operation. The first part of indexing will be for rows and another will be columns (indexes starting from 0 to total no. of rows/columns). For example, first 10 rows for last three columns can be ...
Tutorial: How to Index DataFrames in Pandas - Dataquest Let's explore four methods of label-based dataframe indexing: using the indexing operator [], attribute operator ., loc indexer, and at indexer. Using the Indexing Operator If we need to select all data from one or multiple columns of a pandas dataframe, we can simply use the indexing operator [].
How to Select Columns by Index in a Pandas DataFrame Often you may want to select the columns of a pandas DataFrame based on their index value. If you'd like to select columns based on integer indexing, you can use the .iloc function.. If you'd like to select columns based on label indexing, you can use the .loc function.. This tutorial provides an example of how to use each of these functions in practice.
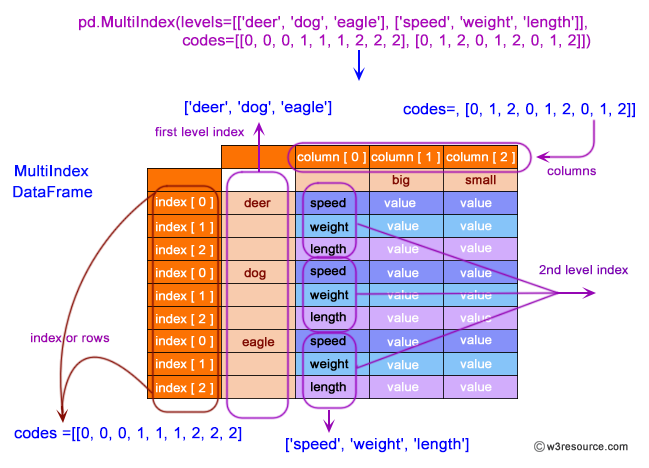
pandas.pydata.org › docs › user_guideMultiIndex / advanced indexing — pandas 1.4.4 documentation A MultiIndex can be created from a list of arrays (using MultiIndex.from_arrays()), an array of tuples (using MultiIndex.from_tuples()), a crossed set of iterables (using MultiIndex.from_product()), or a DataFrame (using MultiIndex.from_frame()). The Index constructor will attempt to return a MultiIndex when it is passed a list of tuples. The ...
How to Select Rows by Index in a Pandas DataFrame - Statology .iloc selects rows based on an integer index. So, if you want to select the 5th row in a DataFrame, you would use df.iloc [ [4]] since the first row is at index 0, the second row is at index 1, and so on. .loc selects rows based on a labeled index. So, if you want to select the row with an index label of 5, you would directly use df.loc [ [5]].
Working with MultiIndex in pandas DataFrame - Spark by {Examples} pandas MultiIndex Key Points - MultiIndex is an array of tuples where each tuple is unique.; You can create MultiIndex from list of arrays, arry of tuples, dataframe e.t.c; The Index constructor will attempt to return a MultiIndex when it is passed a list of tuples.; You can have Multi-level for both Index and Column labels.
python - dynamic indexing using labels in pandas - Stack Overflow I would like to dynamically index elements of a pandas DataFrame using labels. Say I have df1 = pd.DataFrame (np.random.randn (6, 4), index=list ('abcdef'), columns=list ('ABCD')) and I want the element with labels 'a' and 'A'. "Statically" it's easy: df1.loc ['a','A'] But how to do build such a query dynamically at runtime?
How To Find Index Of Value In Pandas Dataframe - DevEnum.com The pandas dataframe. loc method is used to access the row and column by index (label) and column name that is passed by the column label ( Marks) to df. loc [df ['Marks'] = 100 and it will return the rows which satisfy the given condition. Python Program Example import pandas as pd Student_dict = { 'Name': ['Jack', 'Rack', 'Max', 'David'],
Indexing a Pandas DataFrame for people who don't like to remember things It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on. To select a column by its label, we use the .loc[] function. One thing that we can do that makes our commands easy to interpret is to always include both the row index and the column index that we are interested in. In this case, we are interested in all of the rows. To show this, we use a colon. Then, to indicate the column that we're interested in we add its label.
How to Get the Index of a Dataframe in Python Pandas? Method 2: Using index attribute This is the most widely used method to get the index of a DataFrame object. In this method, we will be creating a pandas DataFrame object using the pd.DataFrame () function of as usual. Then we will use the index attribute of pandas DataFrame class to get the index of the pandas DataFrame object.
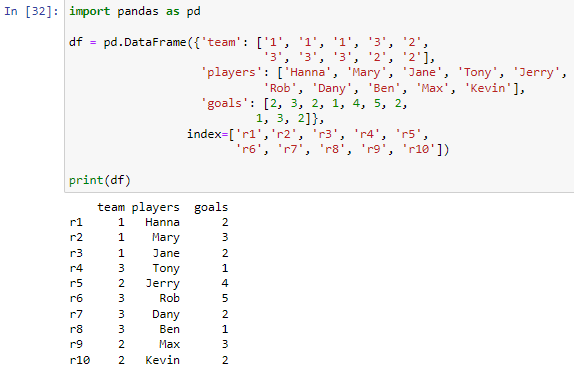
Indexing in Pandas Dataframe using Python | by Kaushik Katari | Towards ... Indexing using .loc method. If we use the .loc method, we have to pass the data using its Label name. Single Row To display a single row from the dataframe, we will mention the row's index name in the .loc method. The whole row information will display like this, Single Row information Multiple Rows
Label-based indexing to the Pandas DataFrame - GeeksforGeeks Indexing plays an important role in data frames. Sometimes we need to give a label-based "fancy indexing" to the Pandas Data frame. For this, we have a function in pandas known as pandas.DataFrame.lookup(). The concept of Fancy Indexing is simple which means, we have to pass an array of indices to access multiple array elements at once.
Pandas DataFrame index Property - W3Schools Definition and Usage. The index property returns the index information of the DataFrame. The index information contains the labels of the rows. If the rows has NOT named indexes, the index property returns a RangeIndex object with the start, stop, and step values.
Indexing and selecting data — pandas 1.4.4 documentation pandas provides a suite of methods in order to have purely label based indexing. This is a strict inclusion based protocol. Every label asked for must be in the index, or a KeyError will be raised. When slicing, both the start bound AND the stop bound are included, if present in the index.
Pandas DataFrame Indexing: Set the Index of a Pandas Dataframe In this method, we can set the index of the Pandas DataFrame object using the pd.Index() and set_index() function. First, we will create a Python list then pass it to the pd.Index() function which returns the DataFrame index object. Then we pass the returned DataFrame index object to the set_index() function to set it as the new index of the DataFrame. Let's implement this through Python code.
Pandas DataFrame Indexing - KDnuggets In pandas data frames, each row also has a name. By default, this label is just the row number. However, you can set one of your columns to be the index of your DataFrame, which means that its values will be used as row labels. We set the column 'name' as our index. It is a common operation to pick out one of the DataFrame's columns to work on.





















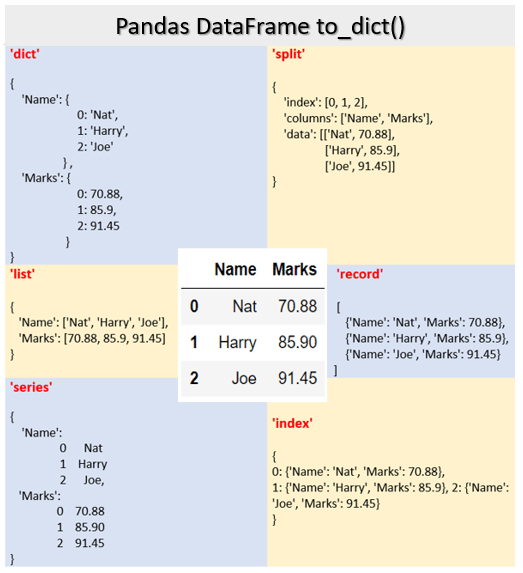



Post a Comment for "43 indexing using labels in dataframe"